The motherboard is the main circuit board of the computer. Every component is connected to it in some way. Motherboards contain slots that hold the processor, expansion cards, and connectors for attaching additional boards. Typically, you will find the following components on the motherboard:
· CPU
· ROM (System BIOS)
· Serial and parallel ports
· Memory
· Chipset
· Clock and Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) battery
· Mass storage interface
· Expansion slots
· Connectors for peripherals including monitor, keyboard, and disk drive(s)
Intel introduced the ATX in 1996 as a replacement for the Baby-AT. It was considered the first dramatic improvement in motherboard form factors used in desktop PCs. The ATX provided a standard, nonproprietary design that was easy to install and maintain. Many modern motherboards use this same form factor (9 inches wide by 12 inches long.)
ATX was the first to integrate components such as the Flash BIOS and I/O logic. The ATX motherboard is half the width of earlier motherboards and contains combinations of ISA and PCI slots, expansion slots that are covered in depth later in this lesson. The power connector for the ATX is one form-molded power connector that prevents it from being connected incorrectly.
Example of ATX Motherboard
· CPU
· ROM (System BIOS)
· Serial and parallel ports
· Memory
· Chipset
· Clock and Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) battery
· Mass storage interface
· Expansion slots
· Connectors for peripherals including monitor, keyboard, and disk drive(s)
Intel introduced the ATX in 1996 as a replacement for the Baby-AT. It was considered the first dramatic improvement in motherboard form factors used in desktop PCs. The ATX provided a standard, nonproprietary design that was easy to install and maintain. Many modern motherboards use this same form factor (9 inches wide by 12 inches long.)
ATX was the first to integrate components such as the Flash BIOS and I/O logic. The ATX motherboard is half the width of earlier motherboards and contains combinations of ISA and PCI slots, expansion slots that are covered in depth later in this lesson. The power connector for the ATX is one form-molded power connector that prevents it from being connected incorrectly.
Example of ATX Motherboard
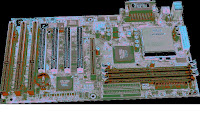
ATX-class and above motherboards may be configured for suspend or power-off functions that are initiated by the operating system. This is especially true with the Microsoft Window XP or higher versions. During suspend, the system goes into a low power state called a sleep mode. Contents of RAM are saved during this state to allow the machine to wake up quickly with all running applications remaining open. The system awakes after the mouse or keyboard is used. During power-off, the system shuts down completely after exiting the operating system.
The following motherboard form factors were developed by Intel as evolutions of the original ATX:
· Micro ATX was built as a smaller design for use in the first small, low-cost computer systems sold in retail stores for under $1,000. The reduced size (9.5 inches wide by 9.5 inches long) allowed for a smaller power supply and few I/O bus expansion slots.
· Flex ATX was introduced as a smaller version of the Micro ATX and considered the least expensive motherboard of the ATX family. It will only support the socket-type CPU (size: 9 inches wide by 7.5 inches long).
· WTX was designed as a high-performance ATX. It is a relatively new board used in high-end servers and workstations. It contains a flex slot that is an enlarged PCI slot used to hold powerful multifunction cards (size: 14 inches wide by 16.75 inches long).
No comments:
Post a Comment